Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM ITGAX / CD11c Antibodies
ITGAX (CD11c) is the integrin alpha X chain protein that functions as a fibrinogen receptor. ITGAX plays a role in monocyte adhesion and chemotaxis, and can induce cellular activation and trigger neutrophil respiratory burst. In cancer, it is positive in leukemia, including the hairy cell, acute nonlymphocytic and B-cell chronic lymphocytic subtypes, and follicular and lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma. In obesity, CD206 and TGAX / CD11c positive macrophages in adipose tissue are correlated with insulin resistance. In immunohistochemistry, ITGAX is found on dendritic cells, monocytes, granulocytes, macrophages, neutrophils, some B cells, as well as roughly half of activated CD4 and CD8 positive T cells. It is commonly used to identify histiocytes and NK cells, and also in the diagnosis of leukemia.
References: The UniProt Consortium. Nucleic Acids Res. 47: D506-515 (2019); Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Jan 4;44(D1):D733-45, PMID:26553804; Diabetes 2010;59:1648, PMID: 20357360; McKusick, Hamosh. Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man, OMIM. Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD. MIM Number: 151510, URL: https://omim.org/ OMIM: 151510; Am J Clin Pathol 2005;124:414, PMID: 16191510; Am J Clin Pathol 1998;110:582, PMID: 9802342;
3 PathPlusTM Antibodies
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(3)
Type
Primary
(3)
Target
ITGAX / CD11c
(3)
Reactivity
Human
(3)
Mouse
(1)
Rat
(1)
Application
IHC
(3)
IHC-P
(2)
WB
(1)
IF
(1)
Host
rabbit
(3)
Product Group
PathPlus Cancer
(3)
Isotype
IgG
(1)
Clonality
polyclonal pc
(3)
Format
Unconjugated
(3)
Epitope
Internal
(2)
Publications
No
(3)

Cancer
Fast Shipping
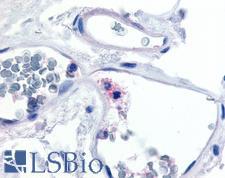
ITGAX / CD11c Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (Internal) Antibody
Human
IHC, IHC-P
Unconjugated
50 µg/$395

Cancer
Fast Shipping
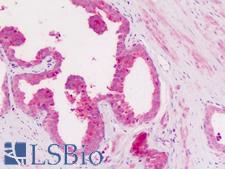
ITGAX / CD11c Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (Internal) Antibody
Human
IHC, IHC-P
Unconjugated
50 µg/$395

Cancer
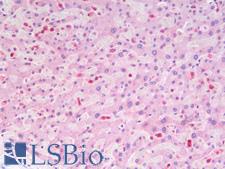
ITGAX / CD11c Rabbit anti-Mouse Polyclonal Antibody
Mouse, Rat, Human
IF, IHC, WB
Unconjugated
60 µl/$460
Viewing 1-3
of 3
product results











