Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM INSR / Insulin Receptor Antibodies
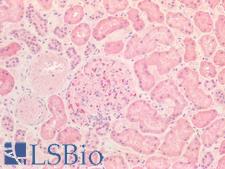
INSR (Insulin receptor, CD22) is a receptor tyrosine kinase that is pivotal to the regulation of glucose homeostasis and mediates the pleiotropic actions of insulin. Binding of insulin leads to phosphorylation of several intracellular substrates, including insulin receptor substrates (IRS1, 2, 3, 4), SHC, GAB1, CBL and other signaling intermediates. Phosphorylation of IRS proteins lead to the activation of two main signaling pathways: the PI3K-AKT/PKB pathway, which is responsible for most of the metabolic actions of insulin, and the Ras-MAPK pathway, which regulates expression of some genes and cooperates with the PI3K pathway to control cell growth and differentiation. In addition to binding insulin, the insulin receptor can bind insulin-like growth factors (IGFI and IGFII). Pathogenic variants in INSR are associated with severe syndromic insulin resistance including the diseases Donohue syndrome and Rabson-Mendenhall syndrome and for increased risk of gestational diabetes. In immunohistochemistry, INSR has cytoplasmic positivity in all tissues throughout the body.
References: The UniProt Consortium. Nucleic Acids Res. 47: D506-515 (2019); Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Jan 4;44(D1):D733-45, PMID:26553804; Ben harouch S, Klar A, Falik Zaccai TC. INSR-Related Severe Syndromic Insulin Resistance. GeneReviews. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle. 2018. URL: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK476444/;
1 PathPlusTM Antibody
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(1)
Type
Primary
(1)
Target
INSR / Insulin Receptor
(1)
Reactivity
Human
(1)
Monkey
(1)
Application
IHC
(1)
IHC-P
(1)
Host
rabbit
(1)
Product Group
PathPlus Cancer
(1)
Clonality
polyclonal pc
(1)
Format
Unconjugated
(1)
Epitope
Internal
(1)
Publications
No
(1)

Cancer
Fast Shipping
INSR / Insulin Receptor Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (Internal) Antibody
Human, Monkey
IHC, IHC-P
Unconjugated
50 µg/$395
Viewing 1-1
of 1
product results










