Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM IGSF4C / CADM4 Antibodies
CADM4 (Cell adhesion molecule 4, IGSF4C, TSLL2) is a membrane glycoprotein of the immunoglobulin superfamily. It is involved in cell-cell interaction, adhesion, regulation of contact inhibition and proliferation. It is expressed in glia and axons, where it functions in Schwann cell and axon interaction. It is also important for the development of the myelin unit in the peripheral nervous system, and absence of CADM4 leads to myelin abnormalities akin to those in Charcot-Marie-Tooth syndrome. CADM4 is thought to be involved in tumor suppression, and expression is lost in breast carcinomas, prostate carcinomas, renal carcinomas and gliomas. In immunohistochemistry, CADM4 has highest cytoplasmic and membranous positivity in neurons in the cerebral cortex, followed by positivity in cell-cell attachment sites in proximal renal tubules, the glandular epithelia of the prostate, the transitional epithelia of the bladder, and a few additional tissues.
References: PLoS One. 2015; 10(4): e0124259, PMID: 25893857; Oncogene. 2006 Mar 9;25(10):1446-53, PMID: 16261159; Int J Cancer. 2012 Mar 15;130(6):1329-37, PMID: 21544807; Oncol Lett. 2018 Feb; 15(2): 2401–2406, PMID: 29434950; J Neurosci. 2013 Jul 3;33(27):10950-61, PMID: 23825401
3 PathPlusTM Antibodies
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(3)
Type
Primary
(3)
Target
IGSF4C / CADM4
(3)
Reactivity
Human
(3)
Mouse
(3)
Rat
(3)
Bat
(1)
Bovine
(1)
Dog
(1)
Horse
(1)
Monkey
(1)
Pig
(1)
Rabbit
(1)
Application
IHC
(2)
IHC-P
(3)
WB
(3)
IF
(1)
Peptide-ELISA
(2)
Host
rabbit
(2)
goat
(1)
Product Group
PathPlus Neuro
(3)
Isotype
IgG
(1)
Clonality
polyclonal pc
(3)
Format
Unconjugated
(3)
Epitope
C-Terminus
(1)
aa339-388
(1)
aa73-83
(1)
Publications
No
(3)

Neuroscience
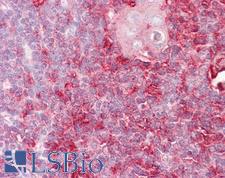
IGSF4C / CADM4 Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (aa339-388) Antibody
Mouse, Rat, Human
IF, IHC, IHC-P, Peptide-ELISA, WB
Unconjugated
50 µl/$460

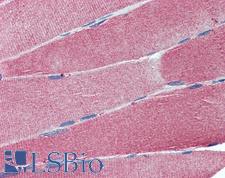
Neuroscience
IGSF4C / CADM4 Goat anti-Human Polyclonal (aa73-83) Antibody
Rabbit, Mouse, Dog, Bovine, Rat, Pig, Horse, Bat, Human, Monkey
IHC, IHC-P, Peptide-ELISA, WB
Unconjugated
50 µg/$375

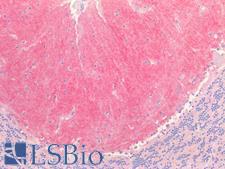
Neuroscience
IGSF4C / CADM4 Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (C-Terminus) Antibody
Mouse, Rat, Human
IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
50 µl/$375
Viewing 1-3
of 3
product results











