Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM GPR1 Antibodies
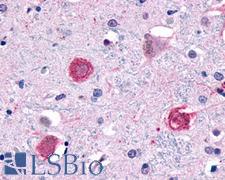
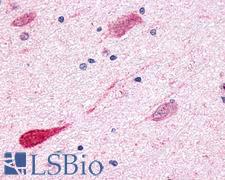
GPR1 is a G protein-coupled receptor that binds chemerin. GPR1 was identified in a search for genes responsible for mediating brain reward and is thought to play a role in drug addiction. It has also been shown to act as an HIV coreceptor in kidney mesangial cells (Tokizawa et al., 2000). In immunohistochemistry, GPR1 has membranous positivity in the basal ganglia, pons and medulla, and corpus callosum in the brain, it is highly expressed in the placenta and is found in reproductive tissues, and it is also present in the esophagus, endocrine tissues, muscle, skin and at low levels throughout the body.
References: The UniProt Consortium. Nucleic Acids Res. 47: D506-515 (2019); Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Jan 4;44(D1):D733-45, PMID:26553804
2 PathPlusTM Antibodies
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(2)
Type
Primary
(2)
Target
GPR1
(2)
Reactivity
Human
(2)
Dog
(1)
Monkey
(1)
Application
IHC
(2)
IHC-P
(2)
ICC
(1)
Host
rabbit
(2)
Product Group
GPCR Database Antibodies
(2)
PathPlus Neuro
(2)
Clonality
polyclonal pc
(2)
Format
Unconjugated
(2)
Epitope
C-Terminus
(2)
Publications
No
(2)

Neuroscience
Fast Shipping
GPR1 Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (C-Terminus) Antibody
Human
IHC, IHC-P
Unconjugated
50 µg/$395

Neuroscience
Fast Shipping
GPR1 Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (C-Terminus) Antibody
Dog, Human, Monkey
ICC, IHC, IHC-P
Unconjugated
50 µg/$395
Viewing 1-2
of 2
product results










