Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM GLS / Glutaminase Antibodies
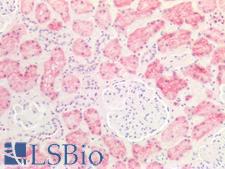
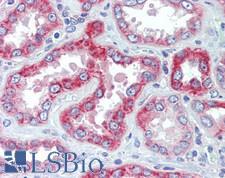
GLS (Glutaminase) is the K-type mitochondrial glutaminase, a phosphate-activated amidohydrolase that catalyzes the hydrolysis of glutamine to glutamate and ammonia. This protein is primarily expressed in axonal terminals of neurons in the brain and in periportal hepatocytes and renal tubules in the kidney. It plays a pivotal role in generating energy for metabolism, synthesizing the brain neurotransmitter glutamate and in maintaining acid-base balance in the kidney. As numerous cancers use glutamate for metabolic and proliferative processes, GLS inhibitors are of interest as potential cancer treatments. In immunohistochemistry, GLS has highest granular cytoplasmic positivity in the brain and kidney, and is also found in the thyroid, lung, gastrointestinal tract, liver, pancreas, reproductive tissues and muscle.
References: International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 16 (9): 22830–55, PMID: 26402672; Kidney Cancer. 2019 Feb 5;3(1):15-29, PMID: 30854496;
2 PathPlusTM Antibodies
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(2)
Type
Primary
(2)
Target
GLS / Glutaminase
(2)
Reactivity
Human
(2)
Mouse
(1)
Rat
(1)
Application
IHC
(1)
IHC-P
(2)
WB
(1)
ELISA
(1)
Host
rabbit
(2)
Product Group
PathPlus Neuro
(2)
Isotype
IgG
(2)
Clonality
polyclonal pc
(2)
Format
Unconjugated
(2)
Publications
No
(2)

Neuroscience
GLS / Glutaminase Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal Antibody
Mouse, Rat, Human
IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
50 µl/$375

Neuroscience
GLS / Glutaminase Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal Antibody
Human
ELISA, IHC, IHC-P
Unconjugated
50 µg/$375
Viewing 1-2
of 2
product results










