Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM FOS / c-FOS Antibodies
FOS (c-Fos, FBJ murine osteosarcoma viral oncogene homolog) is a component of the DNA-binding AP-1 complex together with c-Jun that regulates gene expression and is upregulated in numerous cancers including osteocarcinoma, endometrial cancer, and breast cancer. FOS is involved in the proliferation, differentiation, survival, and angiogenesis of cells, and deregulation of FOS can induce invasion and metastasis via destabilization of these various processes. Separately, FOS is used as a marker of neuronal activity, due to FOS being upregulated after neurons fire action potentials. Its activity is relevant to drug addiction research, as it is upregulated in the prefrontal cortex and nucleus accumbens following use of methamphetamines and psychoactive drugs. In immunohistochemistry, FOS has positive nuclear and cytoplasmic staining in most tissues throughout the body.
References: Histol. Histopathol. 15 (3): 921–8. PMID 10963134; Br. J. Cancer. 99 (8): 1269–75, PMID: 18854825; Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 87 (17): 6912–6, PMID: 2118661; Biol. Psychiatry. 53 (4): 275–83, PMID: 12586446; Journal of Neuroscience Methods. 29 (3): 261–265, PMID: 2507830;
2 PathPlusTM Antibodies
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(2)
Type
Primary
(2)
Target
FOS / c-FOS
(2)
Reactivity
Human
(2)
Mouse
(1)
Rat
(1)
Bovine
(1)
Dog
(1)
Guinea pig
(1)
Horse
(1)
Monkey
(1)
Pig
(1)
Sheep
(1)
Application
IHC
(2)
IHC-P
(2)
WB
(2)
Peptide-ELISA
(2)
Host
rabbit
(1)
goat
(1)
Product Group
PathPlus Neuro
(2)
Isotype
IgG
(1)
Clonality
polyclonal pc
(2)
Format
Unconjugated
(2)
Epitope
aa1-50
(1)
aa283-295
(1)
Publications
No
(1)
Yes
(1)

Neuroscience
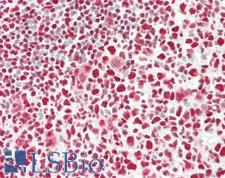
FOS / c-FOS Goat anti-Human Polyclonal (aa283-295) Antibody
Dog, Guinea pig, Sheep, Bovine, Pig, Horse, Human, Monkey
IHC, IHC-P, Peptide-ELISA, WB
Unconjugated
50 µg/$460

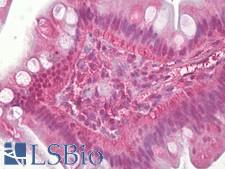
Neuroscience
FOS / c-FOS Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (aa1-50) Antibody
Mouse, Rat, Human
IHC, IHC-P, Peptide-ELISA, WB
Unconjugated
50 µl/$460
Viewing 1-2
of 2
product results










