Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM EGFR Antibodies
EGFR (Epidermal growth factor receptor) is a transmembrane protein kinase that serves as a receptor for epidermal growth factor. Binding of the protein to its ligand induces receptor dimerization, tyrosine autophosphorylation, and activation of signal transduction pathways involved in regulating cell proliferation, differentiation, and cell survival. EGFR is overexpressed in a variety of cancers and correlated with a poor prognosis. Gene amplification of EGFR is a frequent occurrence in some types of breast and other cancers, such as carcinomas of the lung, pancreas, head and neck, and glioblastoma. In breast cancer, roughly half of triple negative and also IBC (inflammatory breast cancer) cases show overexpression of this protein. Expression is generally associated with the basal subtype but is also seen in some luminal B tumors, and is correlated with lower ER/PR expression. Expression of EGFR is cytoplasmic and membranous.
References: Masuda, 2012; Changavi, 2015; Int J Rad Onc Bio Phys 2004 59(Sup):21; Cancers (Basel) 2017 9(5):52
2 PathPlusTM Antibodies
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(2)
Type
Primary
(2)
Target
EGFR
(2)
Reactivity
Human
(2)
Mouse
(1)
Rat
(1)
Application
IHC
(2)
IHC-P
(2)
WB
(1)
Peptide-ELISA
(1)
Host
rabbit
(2)
Product Group
PathPlus Cancer
(2)
PathPlus Cancer Pathology
(2)
Isotype
IgG
(1)
Clonality
polyclonal pc
(2)
Format
Unconjugated
(2)
Epitope
aa1139-1188
(1)
Publications
No
(2)

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
Fast Shipping
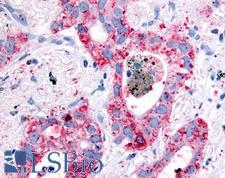
EGFR Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal Antibody
Human
IHC, IHC-P
Unconjugated
50 µg/$460

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
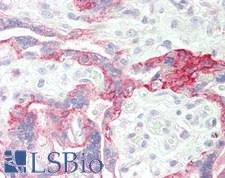
EGFR Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (aa1139-1188) Antibody
Mouse, Rat, Human
IHC, IHC-P, Peptide-ELISA, WB
Unconjugated
100 µl/$375
Viewing 1-2
of 2
product results











