Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
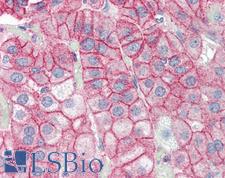
PathPlusTM DLG4 / PSD95 Antibodies
DLG4 (PSD95, SAP-90) is a membrane-associated guanylate kinase functions in anchoring synaptic proteins and stabilizing synaptic modifications during long-term potentiation, and it is required for synaptic plasticity associated with NMDA receptor signaling. It is primarily found in the post synaptic density of neurons. Changes in DLG4 levels affect the ratio of excitatory/inhibitory synapses in hippocampal neurons, and increases in DLG4 promote synaptic strength, synaptogenesis and multiinnervated spine formation. In aging and in neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer’s and Huntington’s disease, downregulation of DLG4 can occur and is associated with changes to hippocampal neuron plasticity and memory deficits. In immunohistochemistry of normal tissue, DLG4 has cytoplasmic positivity in neurons of the central nervous system.
References: Journal of Neuroscience. 1996. 16 (4): 1380–1388, PMID: 8778289; Neuron. 2014 Apr 16;82(2):430-43, PMID: 24742464; Brain. 2017 Dec 1;140(12):3252-3268, PMID: 29155979; J Cell Biol. 2008 Dec 15; 183(6): 1115–1127, PMID: 19075115; J Neurophysiol. 2012 Feb 15; 107(4): 1058–1066, PMID: 22114157;
1 PathPlusTM Antibody
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(1)
Type
Primary
(1)
Target
DLG4 / PSD95
(1)
Reactivity
Human
(1)
Mouse
(1)
Rat
(1)
Application
IHC
(1)
IHC-P
(1)
WB
(1)
ELISA
(1)
IF
(1)
IP
(1)
Host
rabbit
(1)
Product Group
PathPlus Neuro
(1)
Isotype
IgG
(1)
Clonality
polyclonal pc
(1)
Format
Unconjugated
(1)
Epitope
C-Terminus
(1)
Publications
No
(1)

Neuroscience
DLG4 / PSD95 Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (C-Terminus) Antibody
Mouse, Rat, Human
ELISA, IF, IHC, IHC-P, IP, WB
Unconjugated
50 µg/$485
Viewing 1-1
of 1
product results











