Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
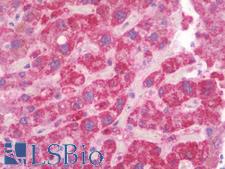
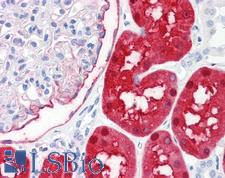
PathPlusTM DDC / DOPA Decarboxylase Antibodies
DDC (Aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase, DOPA decarboxylase, AADC, AAAD) is a lyase that catalyzes the decarboxylation reactions for a number of neurotransmitters and neuromodulators including dopamine, serotonin, histamine and phenylalanine. DDC is required for normal neural function. It can also be a rate-limiting step in dopamine and serotonin synthesis, specifically in Parkinson’s disease patients treated with L-DOPA and in dysthymia or depression patients treated with 5-HTP. Deficiency of DDC is associated with developmental delay, autonomic dysfunction and oculogyric crises, and inherited polymorphisms in DDC may contribute to various neuropsychiatric phenotypes and conditions. In immunohistochemistry of normal tissue, DDC has highest cytoplasmic positivity in renal tissues and is also found in the cerebral cortex, appendix, lung, liver, gastrointestinal tract, prostate, breast and in endocrine and reproductive tissues.
References: BioMed Research International. 2013. Volume 2013 (161456), DOI:10.1155/2013/161456; Neuropsychopharmacology. 2016 Aug; 41(9): 2303–2308; 26924680;
2 PathPlusTM Antibodies
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(2)
Type
Primary
(2)
Target
DDC / DOPA Decarboxylase
(2)
Reactivity
Human
(2)
Mouse
(1)
Rat
(2)
Bovine
(1)
Dog
(1)
Guinea pig
(1)
Sheep
(1)
Application
IHC
(2)
IHC-P
(2)
WB
(2)
ELISA
(1)
IF
(1)
Host
rabbit
(2)
Product Group
PathPlus Neuro
(2)
Isotype
IgG
(1)
Clonality
polyclonal pc
(2)
Format
Unconjugated
(2)
Epitope
N-Terminus
(1)
Publications
No
(1)
Yes
(1)

Neuroscience
DDC / DOPA Decarboxylase Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal Antibody
Mouse, Rat, Human
ELISA, IF, IHC, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
0.05 mg/$460

Neuroscience
DDC / DOPA Decarboxylase Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (N-Terminus) Antibody
Dog, Guinea pig, Sheep, Bovine, Rat, Human
IHC, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
50 µl/$460
Viewing 1-2
of 2
product results










