Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM CTSS / Cathepsin S Antibodies
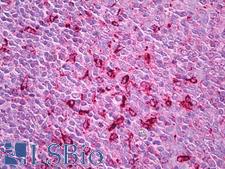
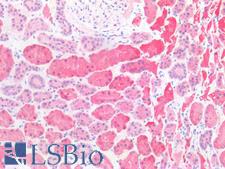
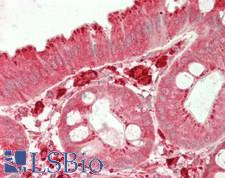
CTSS (Cathepsin S) is a lysosomal cysteine protease of the papain family that functions as a potent elastase in alveolar macrophages and degrades proteins for antigen presentation to the MHC Class II complex. It is found in macrophages, B-lymphocytes, microglia, dendritic cells and populations of epithelial cells. Due to its ability to cleave a wide range of substrates and its role in blood vessel angiogenesis and permeability, it also promotes tumor growth. It is a prognostic marker for a number of cancers including type IV astrocytomas, where it is upregulated, and also a target of inhibition therapies. Suppression of cathpesin S has also been shown to be protective after brain injury. In immunohistochemistry of normal tissue, CTSS has cytoplasmic positivity throughout most of the body.
References: Am J Pathol. 2003 Jul;163(1):175-82, PMID: 12819022; Mediators of Inflammation. 2013 (2013): 187873, PMID: 24282339; Mol Cancer. 2014 Mar 2;13:43, PMID: 24580730; Mol Cancer. 2016 Apr 21;15:29, PMID: 27097645; Neoplasma. 2015;62(1):16-26, PMID: 25563363; Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2009 May-Jun;6(3):149-59, PMID: 19487544
3 PathPlusTM Antibodies
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(3)
Type
Primary
(3)
Target
CTSS / Cathepsin S
(3)
Reactivity
Human
(3)
Mouse
(2)
Application
IHC
(2)
IHC-P
(3)
WB
(1)
ELISA
(2)
Host
rabbit
(2)
mouse
(1)
Product Group
PathPlus Neuro
(3)
Isotype
IgG
(1)
IgG2b
(1)
Clonality
monoclonal mc
(1)
polyclonal pc
(2)
Format
Unconjugated
(3)
Epitope
aa 115-331
(1)
Publications
No
(3)

Neuroscience
CTSS / Cathepsin S Mouse anti-Mouse Monoclonal Antibody
Mouse, Human
ELISA, IHC, IHC-P
Unconjugated
50 µg/$615

Neuroscience
CTSS / Cathepsin S Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal Antibody
Mouse, Human
IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
50 µl/$460

Neuroscience
CTSS / Cathepsin S Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (aa 115-331) Antibody
Human
ELISA, IHC, IHC-P
Unconjugated
50 µg/$375
Viewing 1-3
of 3
product results











