Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM CTSG / Cathepsin G Antibodies
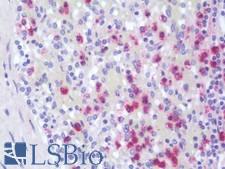
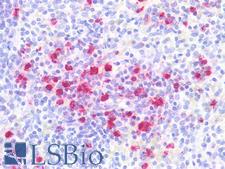
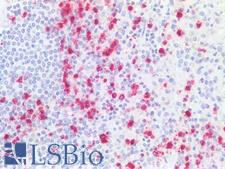
CTSG (Cathepsin G) is a serine protease found in azurophil granules of neutrophilic polymorphonuclear leukocytes. It is thought to function in the remodeling of connective tissue at sites of inflammation. It is involved in neuroinflammation and may be important in neurodegenerative diseases including Alzheimer’s disease. CTSG also plays a role in killing and digesting engulfed pathogens and it is antimicrobial, with bacteriocidal activity against S. aureus and N. gonorrhoeae. CTSG is involved in the pathogenesis of a number of diseases, including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, acute respiratory distress syndrome, cystic fibrosis, rheumatoid arthritis, coronary artery disease, periodontitis, ischemic reperfusion injury, and bone metastasis. Additionally, CTSG variants are correlated with a greater risk of chronic postsurgical pain. In immunohistochemistry, CSTG has cytoplasmic positivity in lymphoid and hematopoietic cells.
References: J Immunol October 1, 2015, 195 (7) 3325-3333, DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1501012; Curr Opin Microbiol. 2015 Feb;23:42-8, PMID: 25461571; Current Opinion in Rheumatology. 19 (3): 289–95, PMID: 17414958; Anatolian Journal of Cardiology. 16 (1): 23–8, PMID: 26467359; Mediators of Inflammation. 2015: 1–10, PMID: 26185359; Anesthesiology. 123 (4): 838–50, PMID: 26270939; J Neuroinflammation. 2018 Aug 27;15(1):240, PMID: 30149799
3 PathPlusTM Antibodies
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(3)
Type
Primary
(3)
Target
CTSG / Cathepsin G
(3)
Reactivity
Human
(3)
Mouse
(1)
Rat
(1)
Application
IHC
(1)
IHC-P
(3)
WB
(3)
Host
rabbit
(3)
Product Group
PathPlus Neuro
(3)
Clonality
polyclonal pc
(3)
Format
Unconjugated
(3)
Epitope
Internal
(1)
aa71-120
(1)
Publications
No
(3)

Neuroscience
CTSG / Cathepsin G Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (aa71-120) Antibody
Human
IHC, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
50 µl/$460

Neuroscience
CTSG / Cathepsin G Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (Internal) Antibody
Human
IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
50 µl/$375

Neuroscience
CTSG / Cathepsin G Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal Antibody
Mouse, Rat, Human
IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
50 µg/$375
Viewing 1-3
of 3
product results











