Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
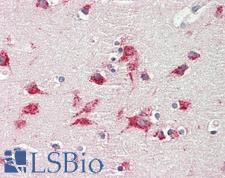
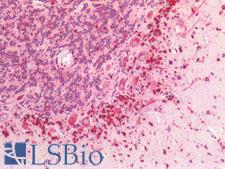
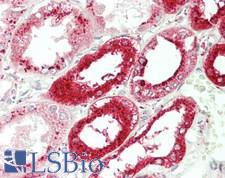
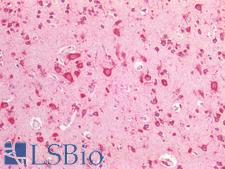
PathPlusTM CTSD / Cathepsin D Antibodies
CTSD (Cathepsin D) is a lysosomal aspartyl protease of the peptidase C1 family that functions to degrade and also activate various intracellular proteins, hormones and growth factors such as VEGFC and VEGFD. Mutations in this gene are involved in the pathogenesis of several diseases, including breast cancer and possibly Alzheimer disease. Mutations and deficiency in CTSD lead to neuronal ceroid-lipofuscinosis (NCL). Loss of CTSD expression has been found to cause oxidative damage to pericytes in the brain, increasing permeability of the blood brain barrier and allowing peripheral blood mononuclear cells to infiltrate in lysosomal storage diseases and NCL. In immunohistochemistry of normal tissue, CTSD has granular cytoplasmic positivity throughout the body.
References: The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1989. 264 (23): 13403–6, PMID: 2760027; Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology. 68 (1): 12–28, PMID: 18396408; Brain. 2006 Jun;129(Pt 6):1353-6, PMID: 16738059; Alzheimer's and Dementia. 2009. 5(4), DOI: 10.1016/j.jalz.2009.04.796; Mol Cell Neurosci. 2015 Jan;64:51-60, PMID: 25496868
4 PathPlusTM Antibodies
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(4)
Type
Primary
(4)
Target
CTSD / Cathepsin D
(4)
Reactivity
Human
(4)
Mouse
(2)
Rat
(1)
Monkey
(1)
Pig
(1)
Application
IHC
(2)
IHC-P
(4)
WB
(4)
IP
(1)
Host
rabbit
(4)
Product Group
PathPlus Cancer
(1)
PathPlus Neuro
(4)
Isotype
IgG
(1)
Clonality
polyclonal pc
(4)
Format
Unconjugated
(4)
Epitope
Internal
(2)
C-Terminus
(1)
aa72-292
(1)
Publications
No
(4)

Neuroscience
CTSD / Cathepsin D Rabbit anti-Mouse Polyclonal (C-Terminus) Antibody
Mouse, Human
IHC, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
100 µl/$375

Neuroscience
CTSD / Cathepsin D Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (Internal) Antibody
Mouse, Rat, Pig, Human
IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
50 µl/$375

Neuroscience
CTSD / Cathepsin D Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (Internal) Antibody
Human, Monkey
IHC, IHC-P, IP, WB
Unconjugated
50 µl/$375

Neuroscience
Cancer
CTSD / Cathepsin D Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (aa72-292) Antibody
Human
IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
50 µl/$375
Viewing 1-4
of 4
product results











