Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
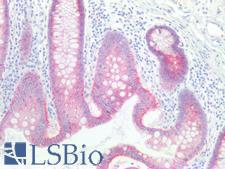
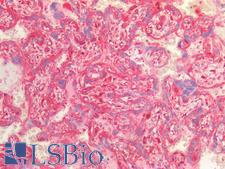
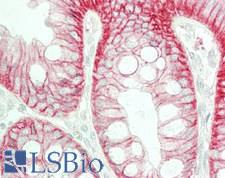
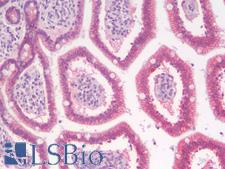
PathPlusTM CTNNB1 / Beta Catenin Antibodies
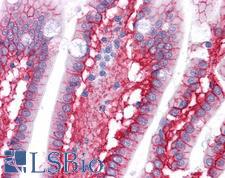
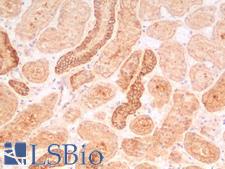
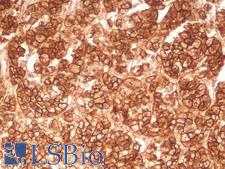
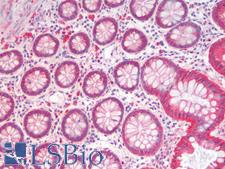
Beta-Catenin (CTNNB1) is a member of the armadillo family of proteins, and part of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. It binds to the cytoplasmic region of the e-cadherin molecule (part of the adherens junction), a complex that is necessary for the creation and maintenance of epithelial layers by regulating cell growth and adhesion, as well as anchoring the actin cytoskeleton. This protein also binds to the APC gene, and mutations in this gene are implicated in colon cancer, papillary thyroid cancer, pilomatrixoma, medulloblastoma, and ovarian cancer. In pathology, CTNNB1 is used to identify desmoid tumors, colorectal cancer, and colon adenomas. It is positive in the membrane of the epithelium of the colon and appendix, weak in endothelial cells, hepatocytes, satellite cells in nerves and follicular dendritic cells in lymph nodes. Staining is membranous in normal colon, and can become nuclear in adenomas and adenocarcinomas.
References: Prakash, J Oral Maxillofac Pathol 2015 19(2):230; Luu 2004, Curr Cancer Drug Targets 4(8):653.
8 PathPlusTM Antibodies
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(8)
Type
Primary
(8)
Target
CTNNB1 / Beta Catenin
(8)
Reactivity
Human
(7)
Mouse
(4)
Rat
(2)
Bovine
(1)
Hamster
(1)
Application
IHC
(3)
IHC-Fr
(1)
IHC-P
(7)
WB
(6)
Flo
(2)
ICC
(1)
IF
(3)
IP
(2)
SWB
(1)
Host
rabbit
(5)
mouse
(3)
Product Group
PathPlus Cancer
(8)
PathPlus Cancer Pathology
(8)
Isotype
IgG
(3)
IgG1
(1)
IgG1,k
(1)
IgG2a
(1)
Clonality
monoclonal mc
(2)
polyclonal pc
(4)
recombinant monoclonal rmc
(2)
Clone
14
(1)
CTNNB1/2030R
(1)
EM-22
(1)
rCTNNB1/2173
(1)
Format
Unconjugated
(8)
Epitope
C-Terminus
(1)
Publications
No
(8)

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
CTNNB1 / Beta Catenin Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal (EM-22) Antibody
Mouse, Hamster, Human
Flo, ICC, IHC, IHC-P, IP, WB
Unconjugated
0.05 mg/$460

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
CTNNB1 / Beta Catenin Rabbit anti-Human Recombinant Monoclonal (CTNNB1/2030R) Antibody
Human
Flo, IF, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
100 µg/$525

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
CTNNB1 / Beta Catenin Mouse anti-Human Recombinant Monoclonal (rCTNNB1/2173) Antibody
Human
IF, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
100 µg/$525

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
CTNNB1 / Beta Catenin Rabbit anti-Mouse Polyclonal Antibody
Mouse, Rat, Human
IF, IHC, WB
Unconjugated
120 µl/$460

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
CTNNB1 / Beta Catenin Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (C-Terminus) Antibody
Mouse, Human
IHC-P, IP, WB
Unconjugated
50 µl/$460

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
CTNNB1 / Beta Catenin Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal Antibody
Mouse, Bovine, Rat, Human
IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
50 µl/$460

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
CTNNB1 / Beta Catenin Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal (14) Antibody
Human
IHC, IHC-Fr, IHC-P
Unconjugated
0.05 ml/$460

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
Fast Shipping
CTNNB1 / Beta Catenin Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal Antibody
IHC-P, SWB
Unconjugated
50 µg/$460
Viewing 1-8
of 8
product results










