Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM CDKN1C / p57 Kip2 Antibodies
CDKN1C is a tight-binding inhibitor of several G1 cyclin/CDK complexes, including cyclin E-CDK2, cyclin D2-CDK4, cyclin A-CDK2 and the mitotic cyclin B-CDC2. It functions as a negative regulator of cell proliferation and may help maintain the non-proliferative state throughout life. Mutations in CDKN1C result in Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome, characterized by early-onset tumorigenesis, and are associated with some sporadic cancers. Loss of functional CDKN1C is also correlated with IMAGe syndrome (or Intrauterine growth restriction, Metaphyseal dysplasia, Adrenal hypoplasia congenita, and Genital anomalies). CDKN1C antibodies are useful for identifying hydatidiform moles, which lack expression of the protein. In immunohistochemistry of normal tissue, CDKN1C has nuclear positivity in the adrenal gland, glomeruli in the kidney, placenta and a few other tissues.
References: Nature Genetics. 44 (7): 737–8, PMID: 22735584; Human Genetics. 100 (5–6): 681–3, PMID: 9341892; The UniProt Consortium. Nucleic Acids Res. 47: D506-515 (2019); Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Jan 4;44(D1):D733-45, PMID:26553804; American Journal of Clinical Pathology. 129 (5): 749–755, PMID: 18426735;
2 PathPlusTM Antibodies
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(2)
Type
Primary
(2)
Target
CDKN1C / p57 Kip2
(2)
Reactivity
Human
(2)
Application
IHC
(1)
IHC-P
(2)
WB
(1)
ELISA
(1)
IF
(1)
Host
rabbit
(1)
mouse
(1)
Product Group
PathPlus Cancer
(2)
PathPlus Cancer Pathology
(2)
Isotype
IgG
(1)
Clonality
monoclonal mc
(1)
polyclonal pc
(1)
Format
Concentrated
(1)
Unconjugated
(2)
Publications
No
(2)

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
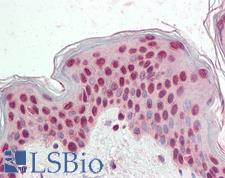
CDKN1C / p57 Kip2 Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal Antibody
Human
ELISA, IF, IHC, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
0.05 mg/$440

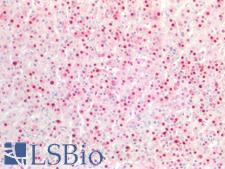
Cancer Pathology
Cancer
CDKN1C / p57 Kip2 Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal (Concentrated) Antibody
Human
IHC-P
Unconjugated, Concentrated
0.05 ml/$460
Viewing 1-2
of 2
product results










