Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM CD44 Antibodies
CD44 is a glycoprotein receptor that is involved in cell adhesion, cell migration, and other cell-cell interactions. It plays a role in many cellular functions including lymphocyte activation, recirculation, and homing, hematopoiesis, and the progression and metastasis of cancer cells. CD44 exists in several isoforms, and the main isoform is expressed ubiquitously in the cytoplasm and membrane of various cell types throughout the body in normal and diseased tissues including cancers and autoimmune diseases. The absence of the main isoform, or the presence of certain other isoforms in cancer cells, is associated with poor prognosis. In immunohistochemistry, CD44 is a marker for squamous epithelium, and in cancer it can distinguish reactive urothelium from carcinoma in situ. It is positive in colorectal cancer, glioma, oligodendroglioma, prostatic small cell carcinoma, squamous cell and adneosquamous carcinoma. Loss of CD44 is a general marker of poor prognosis in cancer.
References: Front Cell Dev Biol. 2017;5:18. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2017.00018; Saudi Med J. 2015;36(3):273-279. doi: 10.15537/smj.2015.3.9622; Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2004;52(1):13-26. PMID: 15053229; Pathol Int. 2012;62(7):463-470. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.2012.02823.x; Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 2017;11(2):77-91. doi: 10.2174/1872213X11666170907111858; Stem Cells Transl Med. 2015;4(9):1033-1043. doi: 10.5966/sctm.2015-0048.
8 PathPlusTM Antibodies
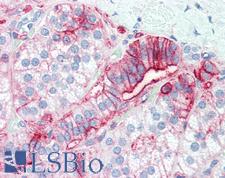
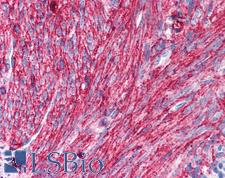
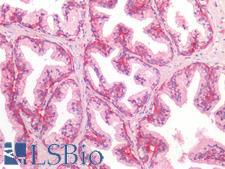
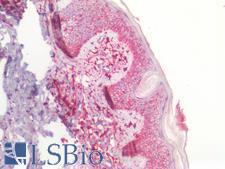
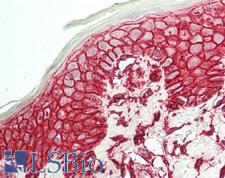
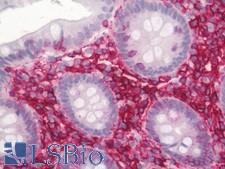
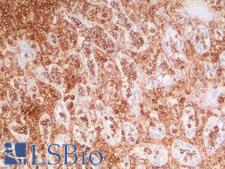
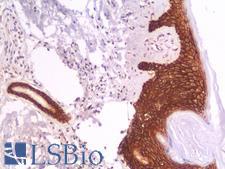
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(8)
Type
Primary
(8)
Target
CD44
(8)
Reactivity
Human
(8)
Mouse
(1)
Canine
(1)
Porcine
(1)
Application
IHC
(4)
IHC-P
(8)
WB
(5)
Flo
(4)
ELISA
(2)
ICC
(2)
IF
(1)
IP
(2)
Peptide-ELISA
(1)
Host
rabbit
(2)
mouse
(5)
goat
(1)
Product Group
PathPlus Cancer
(8)
PathPlus Cancer Pathology
(8)
Isotype
IgG
(2)
IgG1
(4)
IgG2b
(1)
Clonality
monoclonal mc
(4)
polyclonal pc
(2)
recombinant monoclonal rmc
(2)
Clone
8E2F3
(1)
BU52
(1)
HCAM/2875R
(1)
MEM-263
(1)
MEM-85
(1)
rCD44v9/1459
(1)
Format
Azide-free
(1)
Unconjugated
(8)
Epitope
aa1-258
(1)
aa149-163
(1)
Publications
No
(8)

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
CD44 Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal (MEM-85) Antibody
Human
ELISA, Flo, IHC, IHC-P, IP, WB
Unconjugated
0.05 mg/$460

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
CD44 Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal (MEM-263) Antibody
Canine, Porcine, Human
Flo, IHC, IHC-P, IP, WB
Unconjugated
50 µg/$375

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
CD44 Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal (8E2F3) Antibody
Mouse, Human
ELISA, Flo, ICC, IF, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
0.1 ml/$375

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
CD44 Goat anti-Human Polyclonal (aa149-163) Antibody
Human
IHC-P, Peptide-ELISA, WB
Unconjugated
50 µg/$375

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
CD44 Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (aa1-258) Antibody
Human
ICC, IHC, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
100 µl/$375

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
CD44 Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal (Azide-free) (BU52) Antibody
Human
Flo, IHC, IHC-P
Unconjugated, Azide-free
100 µg/$375

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
CD44 Rabbit anti-Human Recombinant Monoclonal (HCAM/2875R) Antibody
Human
IHC-P
Unconjugated
100 µg/$525

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
CD44 Mouse anti-Human Recombinant Monoclonal (rCD44v9/1459) Antibody
Human
IHC-P
Unconjugated
100 µg/$525
Viewing 1-8
of 8
product results











