Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM CD38 Antibodies
CD38 (ADP-ribosyl cyclase 1, cyclic ADP ribose hydrolase) is an enzyme that binds CD31 and synthesizes cyclic ADP-ribose and nicotinate-adenine dinucleotide phosphate. It participates in lymphocyte and endothelial cell adhesion, and regulates cell activation and proliferation depending on the environment. In immunohistochemistry, CD38 can be used to identify plasma cells and plasma-blastic differentiation and to help diagnose myeloma. It is a prognostic marker in HIV+ patients, where higher expression of CD38 and CD8 positive T cells correlates with poor prognosis. In B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia, increased presence on B-CLL cells is also indicative of poor prognosis. In immunohistochemistry of normal tissues, CD38 has strong positivity on plasma cells, and is found on NK cells, B and T cells, committed hematopoietic progenitor cells monocytes, erythroid and myeloid precursors, basophils, neurons, perivascular autonomic nerve terminals, pancreatic islets, small intestinal lacteals, and thymocytes.
References: The UniProt Consortium. Nucleic Acids Res. 47: D506-515 (2019); Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Jan 4;44(D1):D733-45, PMID:26553804; Cytometry B Clin Cytom 2009;76:375, PMID:19422053; Leukemia. 2005 May;19(5):750-8, PMID: 15759031, Brain Res 1995;697:235, PMID: 8593581; Neuroscience 2006;139:1467, PMID: 16580146; Virchows Arch 2002;441:605, PMID: 12461619;
3 PathPlusTM Antibodies
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(3)
Type
Primary
(3)
Target
CD38
(3)
Reactivity
Human
(3)
Monkey
(2)
Application
IHC
(2)
IHC-P
(3)
WB
(1)
ELISA
(1)
Host
rabbit
(2)
mouse
(1)
Product Group
PathPlus Cancer
(3)
PathPlus Cancer Pathology
(3)
Isotype
IgG1
(1)
Clonality
monoclonal mc
(1)
polyclonal pc
(2)
Clone
6E12D4A12
(1)
Format
Unconjugated
(3)
Epitope
C-Terminus
(1)
Internal
(1)
Publications
No
(2)
Yes
(1)

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
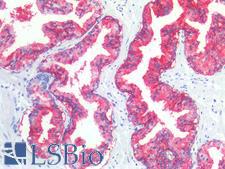
CD38 Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (C-Terminus) Antibody
Human, Monkey
IHC-P
Unconjugated
50 µg/$395

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
Fast Shipping
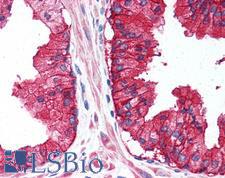
CD38 Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (Internal) Antibody
Human, Monkey
IHC, IHC-P
Unconjugated
50 µg/$395

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
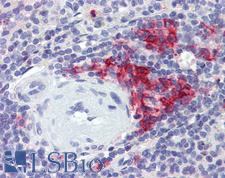
CD38 Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal (6E12D4A12) Antibody
Human
ELISA, IHC, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
50 µl/$460
Viewing 1-3
of 3
product results











