Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
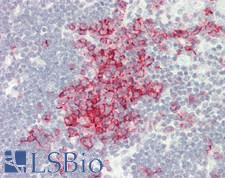
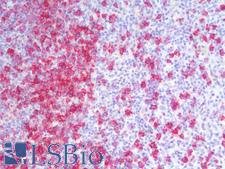
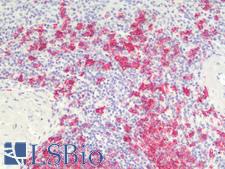
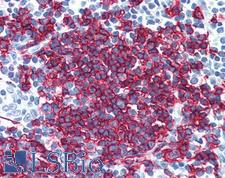
PathPlusTM CD20 Antibodies
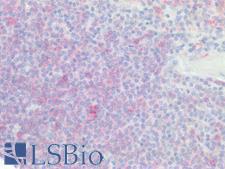
CD20 (MS4A1) is a transmembrane protein that is a member of the membrane-spanning 4A family. It plays a role in the humoral immune response by regulating B-cell proliferation and differentiation. Mutation of the CD20 gene results in impaired B-cell activation and T-cell–dependent humoral immunity. CD20 is expressed at the cell surface during B-cell ontogeny, from late pro–B-cells to memory cells. In normal tissues, it is found in bone marrow and immune system tissues. It is also found in acute and chronic B-cell lymphomas and leukemias, melanoma cancer stem cells, and subsets of Hodgkin lymphoma, myeloma, and thymoma. Staining is used to identify cells of the B-cell lineage and to distinguish B-cell neoplasms (positive) from T-cell neoplasms (negative).
References: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988;85(1):208-212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.208;Cancer Res. 2005;65(20):9328-9337. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-1343;Manual of Diagnostic Antibodies for Immunohistology (2nd ed). London: Greenwich Medical Media; 2003;Janeway's Immunobiology (7th ed). New York: Garland Science; 2008;Textbook of Immunology (2nd ed). Amsterdam: Harwood Academic Publishers GmbH; 1996;J Immunol. 2013;191(6):3112-3118. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1202098.
5 PathPlusTM Antibodies
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(5)
Type
Primary
(5)
Target
CD20
(5)
Reactivity
Human
(4)
Mouse
(1)
Application
IHC
(2)
IHC-P
(5)
WB
(1)
Flo
(2)
ELISA
(1)
IF
(1)
Host
rabbit
(4)
mouse
(1)
Product Group
PathPlus Cancer
(5)
PathPlus Cancer Pathology
(5)
Isotype
IgG
(2)
IgG2a,k
(1)
Clonality
polyclonal pc
(3)
recombinant monoclonal rmc
(2)
Clone
IGEL/1497R
(1)
rIGEL/773
(1)
Format
Unconjugated
(5)
Epitope
C-Terminus
(1)
Publications
No
(5)

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
CD20 Rabbit anti-Mouse Polyclonal Antibody
Mouse, Human
ELISA, IHC, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
50 µg/$460

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
CD20 Mouse anti-Human Recombinant Monoclonal (rIGEL/773) Antibody
Human
Flo, IF, IHC-P
Unconjugated
100 µg/$525

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
CD20 Rabbit anti-Human Recombinant Monoclonal (IGEL/1497R) Antibody
Human
Flo, IHC-P
Unconjugated
100 µg/$525

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
CD20 Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (C-Terminus) Antibody
Human
IHC, IHC-P
Unconjugated
100 µl/$375

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
Fast Shipping
CD20 Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal Antibody
IHC-P
Unconjugated
50 µg/$395
Viewing 1-5
of 5
product results











