Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM AKT1 Antibodies
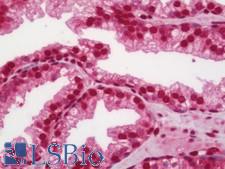
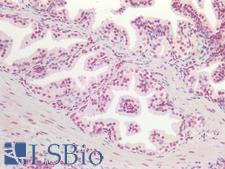
AKT1 (PKB) is a serine/threonine-protein kinase that regulates many processes including metabolism, proliferation, cell survival, growth and angiogenesis. This is mediated through serine and/or threonine phosphorylation of a range of downstream substrates. AKT1 regulates glucose uptake by mediating insulin-induced translocation of the SLC2A4/GLUT4 glucose transporter to the cell surface. Furthermore, AKT1 has an important role in the regulation of NF-kappa-B-dependent gene transcription and positively regulates the activity of CREB1. AKT proteins are important for brain development, and AKT1 is a key modulator of the AKT-mTOR signaling pathway and controls various elements of newborn neuron integration during adult neurogenesis, including correct neuron positioning, speed of radial migration, dendritic development and synapse formation. Downregulation of AKT1 may contribute to neurodegeneration in diseases such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease. Finally, mutations in AKT1 are causative for Proteus syndrome. In immunohistochemistry of normal tissue, AKT1 has high nuclear positivity in all tissues throughout the body.
References: N. Engl. J. Med. 2011. 365 (7): 611–9, PMID: 21793738; Free Radic Biol Med. 2014 Sep;74:118-28, PMID: 24933620; Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 May 24;113(21):E2955-64, PMID: 27170189;
2 PathPlusTM Antibodies
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(2)
Type
Primary
(2)
Target
AKT1
(2)
Reactivity
Human
(2)
Mouse
(2)
Rat
(1)
Application
IHC
(1)
IHC-P
(2)
WB
(2)
Peptide-ELISA
(1)
Host
rabbit
(2)
Product Group
PathPlus Neuro
(2)
Isotype
IgG
(1)
Clonality
polyclonal pc
(2)
Format
Unconjugated
(2)
Epitope
aa416-465
(1)
Publications
No
(2)

Neuroscience
AKT1 Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (aa416-465) Antibody
Mouse, Rat, Human
IHC, IHC-P, Peptide-ELISA, WB
Unconjugated
100 µl/$375

Neuroscience
AKT1 Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal Antibody
Mouse, Human
IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
50 µg/$375
Viewing 1-2
of 2
product results











