Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM ADORA2A/Adenosine A2A Receptor Antibodies
ADORA2A (Adenosine A2A Receptor) is a member of the guanine nucleotide-binding protein (G protein)-coupled receptor (GPCR) superfamily. It is a receptor for adenosine and is also targeted by caffeine. ADORA2A amplifies intracellular cAMP levels after binding adenosine, and it is important for cardiac rhythm and circulation, cerebral and renal blood flow, immune function, pain regulation, and sleep. Furthermore, natural increases in ADORA2A over time may be relevant to age-related decline in memory, and abrogation of the protein results in memory enhancements in mice. Along these lines, it is relevant to long-term memory storage and loss, and is thought to play a role in memory loss and the pathogenesis of related neurodegenerative disorders and inflammatory diseases. Levels of expression of this receptor have been found to be upregulated in astrocytes in Alzheimer’s disease patients and also in the early stages of Parkinson’s disease. In immunohistochemistry of normal tissue, ADORA2A has selective membranous positivity in the caudate nucleus in the brain and on populations of cells in the thymus, and is also expressed in vasculature and on platelets.
References: Neurobiol Dis. 2014 Sep;69:206-14, PMID: 24892887; Nat Neurosci. 2015 Mar;18(3):423-34, PMID: 25622143; Nat Neurosci. 2015 Mar;18(3):423-34, PMID: 25622143; Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man, OMIM®. Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD. MIM Number: 102776. https://omim.org;
3 PathPlusTM Antibodies
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(3)
Type
Primary
(3)
Target
ADORA2A/Adenosine A2A Receptor
(3)
Reactivity
Human
(3)
Mouse
(2)
Rat
(2)
Dog
(1)
Guinea pig
(1)
Monkey
(1)
Rabbit
(1)
Application
IHC
(3)
IHC-P
(3)
WB
(2)
Flo
(1)
ICC
(1)
IF
(1)
IHC-Pfa
(1)
Host
rabbit
(2)
mouse
(1)
Product Group
GPCR Database Antibodies
(1)
PathPlus Neuro
(3)
Isotype
IgG2a
(1)
Clonality
monoclonal mc
(1)
polyclonal pc
(2)
Clone
7F6-G5-A2 / 7F6
(1)
Format
Unconjugated
(3)
Epitope
3rd Intracellular Domain
(1)
C-Terminus
(1)
Internal
(1)
Publications
No
(3)

Neuroscience
Fast Shipping
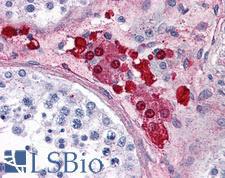
ADORA2A/Adenosine A2A Receptor Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (C-Terminus) Antibody
Human
IHC, IHC-P
Unconjugated
50 µg/$395

Neuroscience
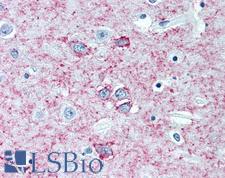
ADORA2A/Adenosine A2A Receptor Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal (3rd Intracellular Domain) (7F6-G5-A2 / 7F6 ) Antibody
Rabbit, Mouse, Dog, Guinea pig, Rat, Human
Flo, IHC, IHC-P, IHC-Pfa, WB
Unconjugated
50 µg/$635

Neuroscience
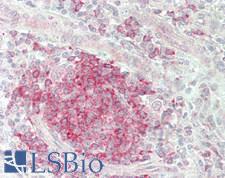
ADORA2A/Adenosine A2A Receptor Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (Internal) Antibody
Mouse, Rat, Human, Monkey
ICC, IF, IHC, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
50 µl/$375
Viewing 1-3
of 3
product results











