Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM Adiponectin Antibodies
Adiponectin (ADIPOQ) is an important adipokine involved in the control of fat metabolism and insulin sensitivity, with direct anti-diabetic, anti-atherogenic and anti-inflammatory activities. This protein serves to stimulate AMPK phosphorylation and activation in the liver and in skeletal muscle, which enhances glucose utilization and fatty-acid combustion. It may play a role in cell growth, angiogenesis and tissue remodeling by binding and sequestering various growth factors with distinct binding affinities depending on the type of complex (LMW, MMW or HMW). Mutations in this gene are associated with intracranial atherosclerosis, a major cause of stroke. Additionally, knockout studies in rats have shown that adiponectin may be involved in regulating sensitivity to psychomotor stimulants and susceptibility to drug effects in addiction. In immunohistochemistry, adiponectin stains the cytoplasm and plasma of a number of tissues, including adipose and soft tissue, muscle, the gastrointestinal tract, the kidney, breast, and female reproductive tissues.
References: Int J Neurosci. 2017 May;127(5):427-432, PMID: 27224208, Genes Brain Behav. 2017 Sep;16(7):686-698, PMID: 28387990
2 PathPlusTM Antibodies
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(2)
Type
Primary
(2)
Target
Adiponectin
(2)
Reactivity
Human
(2)
Application
IHC
(2)
IHC-P
(2)
WB
(2)
ELISA
(1)
Host
mouse
(1)
goat
(1)
Product Group
PathPlus Neuro
(2)
Isotype
IgG
(1)
IgG1
(1)
Clonality
monoclonal mc
(1)
polyclonal pc
(1)
Clone
2C9
(1)
Format
Unconjugated
(2)
Epitope
aa19-244
(1)
Publications
No
(2)

Neuroscience
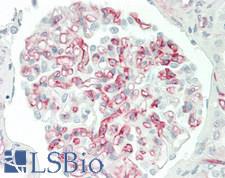
Adiponectin Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal (aa19-244) (2C9) Antibody
Human
IHC, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
50 µl/$440

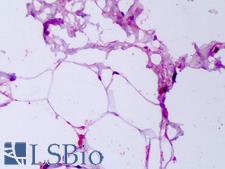
Neuroscience
Adiponectin Goat anti-Human Polyclonal Antibody
Human
ELISA, IHC, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
50 µg/$485
Viewing 1-2
of 2
product results










