Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
| Catalog Number | Size | Price |
|---|---|---|
| LS-C188526-0.5 | 0.5 mg (1 mg/ml) | $493 |
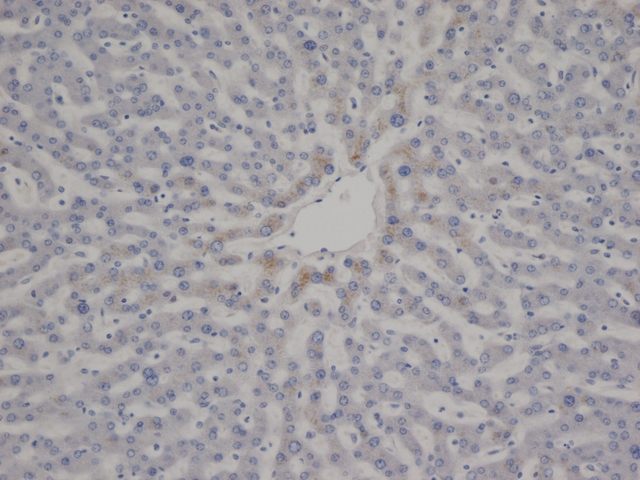
Monoclonal Mouse anti‑Human VWF / Von Willebrand Factor Antibody (clone RFF‑VIII R/1, IHC) LS‑C188526
Monoclonal Mouse anti‑Human VWF / Von Willebrand Factor Antibody (clone RFF‑VIII R/1, IHC) LS‑C188526
Note: This antibody replaces LS-C188527
Antibody:
VWF / Von Willebrand Factor Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal (RFF-VIII R/1) Antibody
Application:
IHC-Fr, ELISA, Purif, RIA
Reactivity:
Human
Format:
Unconjugated, Unmodified
Toll Free North America
 (800) 227-6666
(800) 227-6666
For Research Use Only
Overview
Antibody:
VWF / Von Willebrand Factor Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal (RFF-VIII R/1) Antibody
Application:
IHC-Fr, ELISA, Purif, RIA
Reactivity:
Human
Format:
Unconjugated, Unmodified
Specifications
Description
Von Willebrand Factor antibody LS-C188526 is an unconjugated mouse monoclonal antibody to human Von Willebrand Factor (VWF). Validated for ELISA, IHC, Purif and RIA.
Target
Human VWF / Von Willebrand Factor
Synonyms
VWF | Coagulation factor VIII VWF | F8VWF | VWD | Von Willebrand factor | factor VIII-related antigen | Factor VIII-R | Factor VIII-R Ag | VIII R AG
Host
Mouse
Reactivity
Human
(tested or 100% immunogen sequence identity)
Clonality
IgG1
Monoclonal
Clone
RFF-VIII R/1
Conjugations
Unconjugated
Purification
Protein G purified
Modifications
Unmodified
Immunogen
Human Factor VIII complex partially purified from Factor VIII concentrate.
Specificity
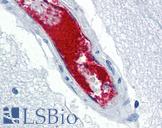
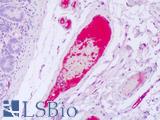
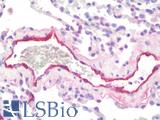
Recognizes human von Willebrand factor (vWF), also known as Factor VIII related antigen, a blood glycoprotein involved in blood coagulation. It stabilizes circulating Factor VIII by binding to it and protecting it from cleavage and delivers it to sites of vascular injury. vWF also promotes the adhesion of platelets to sites of vascular damage by forming a molecular bridge between collagen on exposed endothelial cells and the GPIb binding sites of platelets circulating in the blood. vWF circulates in the blood as large multimers, with each monomer (250kD) containing a number of specific domains. Hereditary or acquired defects in vWF lead to von Willebrand disease (vWD), characterized by varying degrees of susceptibility to bleeding. Symptoms might include nosebleeds, bleeding gums, easy bruising, menorrhagia or gastrointestinal bleeding. Various forms of vWD exist with differing severities, determined by the type of defect. Clone RF-VIII R/1 has a high affinity for an epitope within the platelet GPIb-binding site that is responsible for biological activity. As such the antibody is a potent inhibitor of vWF activity. It can completely neutralize ristocetin-induced platelet aggregation and ristocetin-induced binding of vWF to platelets. It also inhibits platelet adhesion to glass beads. The epitope recognized is present only on the intact multimeric form of vWF and is abolished by mild denaturation with SDS. The antibody does not recognize human Factor VIII. Clone RF-VIII R/1 may be used as a capture antibody in immunoassays for vWF in combination with clone RFF-VIII R/2 as a detection reagent.
Applications
- IHC - Frozen
- ELISA
- Purification
- Radioimmunoassay
|
Performing IHC? See our complete line of Immunohistochemistry Reagents including antigen retrieval solutions, blocking agents
ABC Detection Kits and polymers, biotinylated secondary antibodies, substrates and more.
|
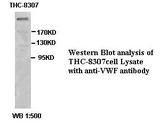
Failed Applications
- Western blot
Presentation
PBS, 0.09% Sodium Azide
Storage
Store at 4°C or at -20°C. Store undiluted. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. Microcentrifugation recommended if solution contains precipitate.
Restrictions
For research use only. Intended for use by laboratory professionals.
About VWF / Von Willebrand Factor
Publications (0)
Customer Reviews (0)
Featured Products
Species:
Human
Applications:
IHC, IHC - Paraffin, IHC - Frozen, Western blot, ELISA
Species:
Human
Applications:
IHC, IHC - Paraffin, ELISA, Immunoelectrophoresis
Species:
Human
Applications:
IHC, IHC - Paraffin, ELISA, Immunoelectrophoresis
Species:
Rat, Human
Applications:
IHC, IHC - Paraffin
Species:
Human
Applications:
ELISA, Immunoelectrophoresis
Request SDS/MSDS
To request an SDS/MSDS form for this product, please contact our Technical Support department at:
Technical.Support@LSBio.com
Requested From: United States
Date Requested: 4/1/2025
Date Requested: 4/1/2025