Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
| Catalog Number | Size | Price |
|---|---|---|
| LS-C500194-50 | 50 µg | $294 |
| LS-C500194-100 | 100 µg | $360 |
Polyclonal Rabbit anti‑Human NRG1 / Heregulin / Neuregulin Antibody (FITC) LS‑C500194
Polyclonal Rabbit anti‑Human NRG1 / Heregulin / Neuregulin Antibody (FITC) LS‑C500194
Antibody:
NRG1 / Heregulin / Neuregulin Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (FITC) Antibody
Application:
ELISA
Reactivity:
Human
Format:
FITC, Unmodified
Other formats:
Toll Free North America
 (800) 227-6666
(800) 227-6666
For Research Use Only
Overview
Antibody:
NRG1 / Heregulin / Neuregulin Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (FITC) Antibody
Application:
ELISA
Reactivity:
Human
Format:
FITC, Unmodified
Other formats:
Specifications
Description
Neuregulin antibody LS-C500194 is an FITC-conjugated rabbit polyclonal antibody to human Neuregulin (NRG1 / Heregulin). Validated for ELISA.
Target
Human NRG1 / Heregulin / Neuregulin
Synonyms
NRG1 | ARIA | GGF | GGF2 | Glial growth factor | Heregulin | HRGA | MSTP131 | NDF | Neu differentiation factor | Neuregulin 1 type IV beta 3 | Neuregulin 1 type IV beta 1a | HRG1 | NRG-1 | SMDF | Neuregulin 1 | Pro-NRG1 | HGL | MST131
Host
Rabbit
Reactivity
Human
(tested or 100% immunogen sequence identity)
Clonality
IgG
Polyclonal
Conjugations
Purification
Protein G purified
Modifications
Unmodified
Immunogen
Recombinant human Pro-neuregulin-1, membrane-bound isoform protein (75-176AA)
Specificity
Direct ligand for ERBB3 and ERBB4 tyrosine kinase receptors. Concomitantly recruits ERBB1 and ERBB2 coreceptors, resulting in ligand-stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation and activation of the ERBB receptors. The multiple isoforms perform diverse functions such as inducing growth and differentiation of epithelial, glial, neuronal, and skeletal muscle cells; inducing expression of acetylcholine receptor in synaptic vesicles during the formation of the neuromuscular junction; stimulating lobuloalveolar budding and milk production in the mammary gland and inducing differentiation of mammary tumor cells; stimulating Schwann cell proliferation; implication in the development of the myocardium such as trabeculation of the developing heart. Isoform 10 may play a role in motor and sensory neuron development. Binds to ERBB4 (PubMed:10867024, PubMed:7902537). Binds to ERBB3 (PubMed:20682778). Acts as a ligand for integrins and binds (via EGF domain) to integrins ITGAV:ITGB3 or ITGA6:ITGB4. Its binding to integrins and subsequent ternary complex formation with integrins and ERRB3 are essential for NRG1-ERBB signaling. Induces the phosphorylation and activation of MAPK3/ERK1, MAPK1/ERK2 and AKT1 (PubMed:20682778). Ligand-dependent ERBB4 endocytosis is essential for the NRG1-mediated activation of these kinases in neurons (By similarity).
Applications
- ELISA
- Applications tested for the base form of this product only
Presentation
PBS, pH 7.4, 0.03% Proclin 300, 50% glycerol.
Storage
Short term: -20°C; Long term: -80°C; Avoid freeze-thaw cycles.
Restrictions
For research use only. Intended for use by laboratory professionals.
About NRG1 / Heregulin / Neuregulin
Publications (0)
Customer Reviews (0)
Featured Products
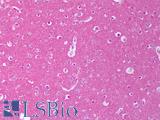
Species:
Human
Applications:
IHC, IHC - Paraffin, Western blot, ELISA
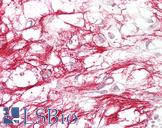
Species:
Human
Applications:
IHC, IHC - Paraffin, Western blot, Flow Cytometry
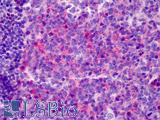
Species:
Human, Mouse, Rat
Applications:
IHC, IHC - Paraffin, Western blot, Peptide Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Species:
Human
Applications:
Western blot
Species:
Human
Applications:
Western blot, ELISA
Species:
Human, Monkey
Applications:
IHC, IHC - Paraffin
Request SDS/MSDS
To request an SDS/MSDS form for this product, please contact our Technical Support department at:
Technical.Support@LSBio.com
Requested From: United States
Date Requested: 12/27/2024
Date Requested: 12/27/2024