Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
| Catalog Number | Size | Price |
|---|---|---|
| LS-C45438-0.2 | 0.2 mg (1 mg/ml) | $471 |
Monoclonal Mouse anti‑Human CD58 Antibody (clone BRIC5, Cytoplasmic Domain, WB) LS‑C45438
Monoclonal Mouse anti‑Human CD58 Antibody (clone BRIC5, Cytoplasmic Domain, WB) LS‑C45438
Note: This antibody replaces LS-C58724
Antibody:
CD58 Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal (Cytoplasmic Domain) (BRIC5) Antibody
Application:
WB, Flo
Reactivity:
Human
Format:
Unconjugated, Unmodified
Toll Free North America
 (800) 227-6666
(800) 227-6666
For Research Use Only
Overview
Antibody:
CD58 Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal (Cytoplasmic Domain) (BRIC5) Antibody
Application:
WB, Flo
Reactivity:
Human
Format:
Unconjugated, Unmodified
Specifications
Description
CD58 antibody LS-C45438 is an unconjugated mouse monoclonal antibody to human CD58 (Cytoplasmic Domain). Validated for Flow and WB.
Target
Human CD58
Synonyms
CD58 | CD58 antigen | AG3 | LFA-3 | LFA3 | Surface glycoprotein LFA-3 | Surface glycoprotein lfa3 | CD58 molecule
Host
Mouse
Reactivity
Human
(tested or 100% immunogen sequence identity)
Clonality
IgG2a
Monoclonal
Clone
BRIC5
Conjugations
Unconjugated
Purification
Protein G purified
Modifications
Unmodified
Immunogen
Human erythrocytes.
Epitope
Cytoplasmic Domain
Specificity
CD58, or LFA-3, is a membrane glycoprotein of 55-70kD. It occurs in two forms, one transmembrane with a cytoplasmic domain, the other form anchored in the membrane via a glycosylphosphatidylinositol tail. The complete amino acid sequence of both forms has been deduced from cDNA. It is heavily N-glycosylated. CD58 is a cell adhesion molecule which plays a critical role in facilitation of antigen specific recognition through interaction with CD2 on T lymphocytes[1]. It is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily of molecules. CD58 has a wide tissue distribution, being present on erythrocytes, platelets, monocytes, a subset of lymphocytes, bone marrow cells, epithelium and endothelial cells[2]. There are approximately 5000 CD58 molecules on each erythrocyte. There is reduced expression of CD58 on hemopoietic cells in individuals with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. BRIC5 was produced in response to erythrocytes. The functional affinity of BRIC5 binding to erythrocytes is 4 x 108 M-1. Reacts by immunoblotting to non-reduced erythrocyte membranes. BRIC5 is an indirect hemagglutinin. The antigen on erythrocytes is Pronase sensitive. BRIC5 inhibits T cell rosetting.
Applications
- Western blot
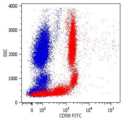
- Flow Cytometry (1:10)
Failed Applications
- IHC - Paraffin
- IHC - Frozen
Usage
Flow Cytometry: Use 10 ul of the suggested working dilution to label 10^6 cells in 100 ul. Method sheets are available on request.
Presentation
0.09% Sodium Azide
Storage
Store at 4°C or at -20°C. Store undiluted. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. Microcentrifugation recommended if solution contains precipitate.
Restrictions
For research use only. Intended for use by laboratory professionals.
About CD58
Publications (0)
Customer Reviews (0)
Featured Products
Species:
Human
Applications:
IHC, IHC - Paraffin, Immunofluorescence, Western blot, ELISA
Species:
Human
Applications:
Flow Cytometry, Functional Assay
Species:
Human
Applications:
IHC, Immunoprecipitation, Flow Cytometry, Cytotoxic Assay
Request SDS/MSDS
To request an SDS/MSDS form for this product, please contact our Technical Support department at:
Technical.Support@LSBio.com
Requested From: United States
Date Requested: 12/21/2024
Date Requested: 12/21/2024