order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
MYOG / Myogenin
myogenin (myogenic factor 4)
Acts as a transcriptional activator that promotes transcription of muscle-specific target genes and plays a role in muscle differentiation, cell cycle exit and muscle atrophy. Essential for the development of functional embryonic skeletal fiber muscle differentiation. However is dispensable for postnatal skeletal muscle growth; phosphorylation by CAMK2G inhibits its transcriptional activity in respons to muscle activity. Required for the recruitment of the FACT complex to muscle-specific promoter regions, thus promoting gene expression initiation. During terminal myoblast differentiation, plays a role as a strong activator of transcription at loci with an open chromatin structure previously initiated by MYOD1. Together with MYF5 and MYOD1, co-occupies muscle-specific gene promoter core regions during myogenesis. Cooperates also with myocyte-specific enhancer factor MEF2D and BRG1-dependent recruitment of SWI/SNF chromatin-remodeling enzymes to alter chromatin structure at myogenic late gene promoters. Facilitates cell cycle exit during terminal muscle differentiation through the up-regulation of miR-20a expression, which in turn represses genes involved in cell cycle progression. Binds to the E-box containing (E1) promoter region of the miR-20a gene. Plays also a role in preventing reversal of muscle cell differentiation. Contributes to the atrophy-related gene expression in adult denervated muscles. Induces fibroblasts to differentiate into myoblasts.
| Gene Name: | myogenin (myogenic factor 4) |
| Synonyms: | MYOG, BHLHc3, Myogenin, MYF4, Myogenic factor 4, Myf-4, Myogenin (myogenic factor 4) |
| Target Sequences: | NM_002479 NP_002470.2 P15173 |

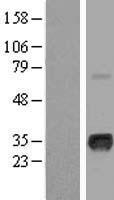
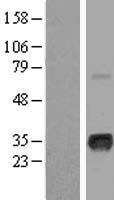
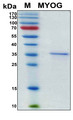
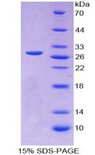
If you do not find the reagent or information you require, please contact Customer.Support@LSBio.com to inquire about additional products in development.









